

APRA CPS 230 is the Prudential Standard for Operational Risk Management. It aims to ensure that APRA-regulated entities manage operational risks effectively, maintain critical operations during disruptions, and meet compliance obligations. CPS 230 applied from 1 July 2025. For pre-existing service provider contracts, requirements apply from the earlier of the next renewal date or 1 July 2026.
Its scope covers a range of operational risks, including legal, regulatory, compliance, conduct, technology, data and change management.
It also requires you to identify your “critical operations”, set Board-approved tolerance levels (e.g. maximum outage and data loss), and maintain these through disruption with a tested Business Continuity Plan (BCP).
APRA CPS 230 impacts vendor-facing teams such as Procurement, Vendor Management, and Legal by necessitating the effective management of operational risks and disruptions - including those arising from service providers.
The most stringent obligations apply to material service providers (MSPs): those relied on to perform a critical operation or that expose the entity to material operational risk. Some services are presumed material unless otherwise justified.APRA CPS 230 requires these teams to identify, assess, and manage risks that may result from inadequate or failed internal processes or systems, actions or inactions of people, or external drivers and events.
This includes managing risks from fourth parties (your providers’ key subcontractors) where those dependencies are material.
The key requirements of CPS 230 are that an APRA-regulated entity must:
Existing contracts must be uplifted at their next renewal or by 1 July 2026.
APRA CPS 230 imposes several requirements on vendors and service providers:
Where APRA considers that an APRA-regulated entity’s operational risk management has material weaknesses, it may:
The Board of your business is ultimately accountable for the oversight of an entity’s operational risk management but senior management is responsible for it across the end-to-end process for all business operations.
Achieving compliance consistently requires more than manual oversight or siloed tools. It calls for a unified approach, one that brings together contract governance and third-party risk in a single framework.
Gatekeeper, powered by LuminIQ agents, provides exactly that.
Every third party is screened against risk criteria before engagement begins. Obligations and attestations are then continuously monitored to ensure nothing slips through the cracks. By maintaining a single source of truth across contracts and vendors, leadership teams can evidence compliance, manage concentration risk, and demonstrate operational resilience at board level.
All your existing vendor contracts should be in your contract repository, linked to a specific service provider.
You’ll now have to carry out checks across all of your vendor contracts to ensure that your contracts contain provisions around the following:
Within Gatekeeper, you’ll be able to access every vendor contract via the contract record, where you’ll find your “master” contract. Any additional contract documents will be found in the files area, and you can click the eyeball to see them.
Lumin Insights provides a full AI summary of your contracts so you can quickly review whether or not the contract contains CPS 230-compliant clauses.
To track all of this in Gatekeeper, we could create an APRA CPS 230 custom data point to assess each contract's compliance level.
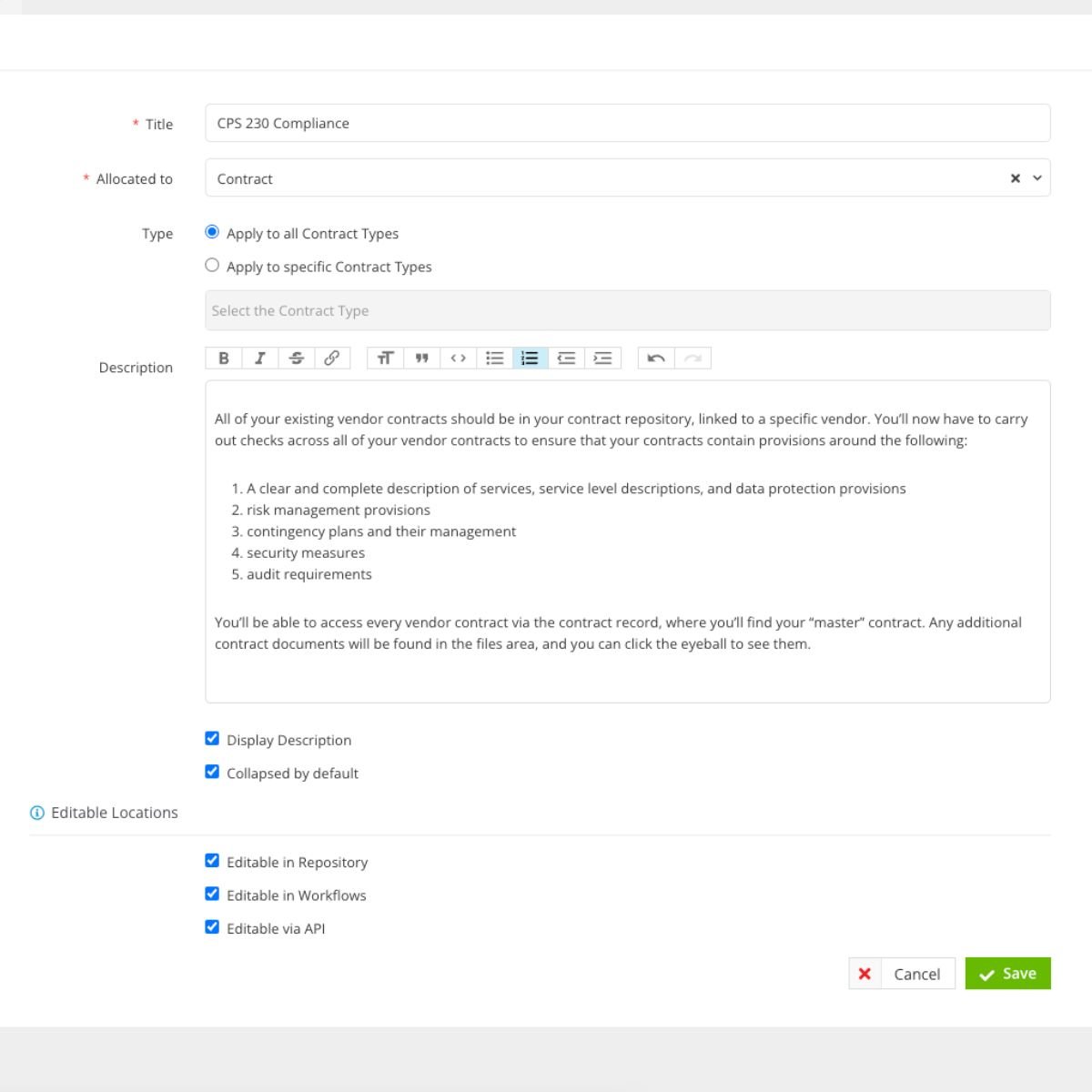 CPS 230 Custom Data Section Creation
CPS 230 Custom Data Section Creation
I’ve gone for these as an example here:
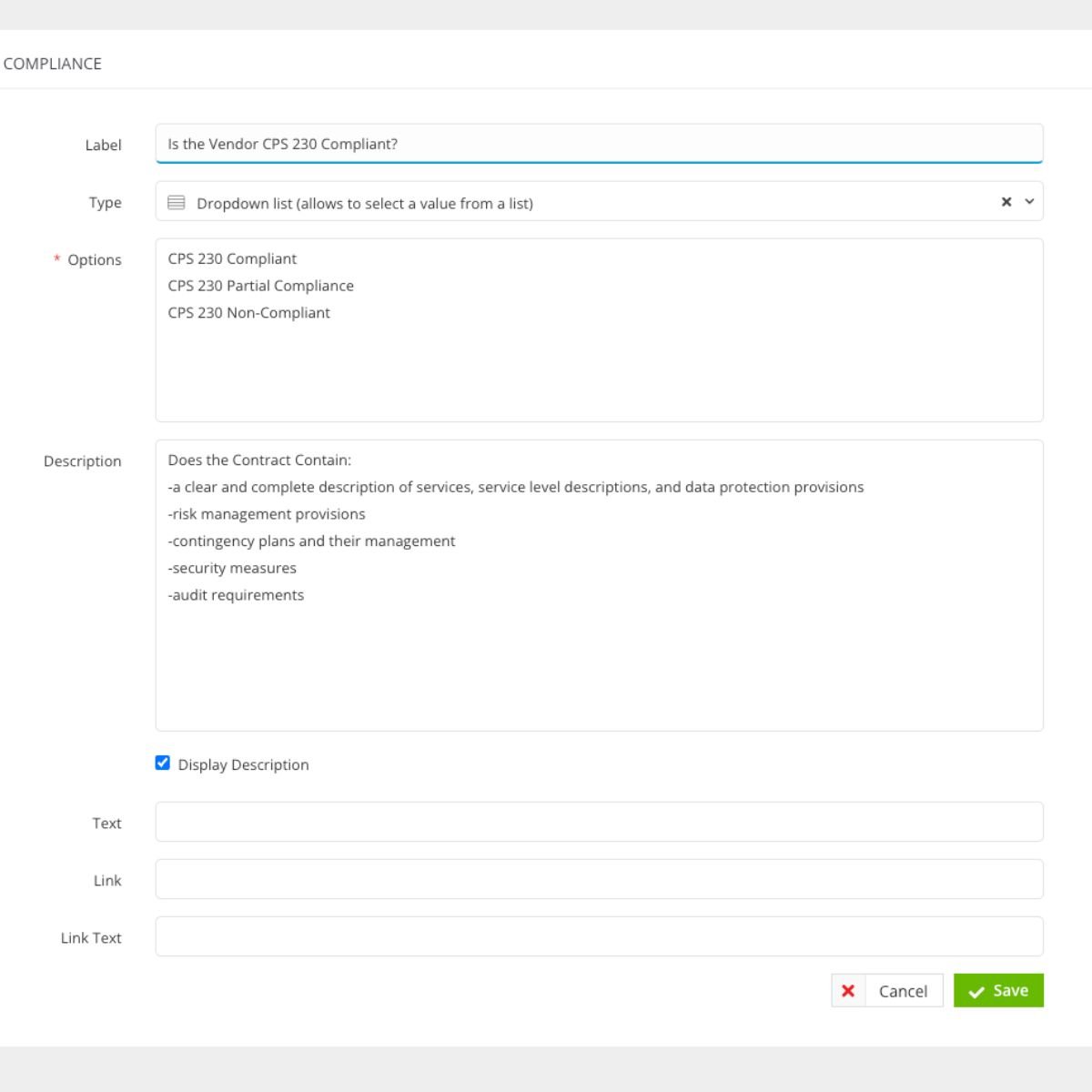 CPS 230 Custom Data Dropdown Status Creation
CPS 230 Custom Data Dropdown Status Creation
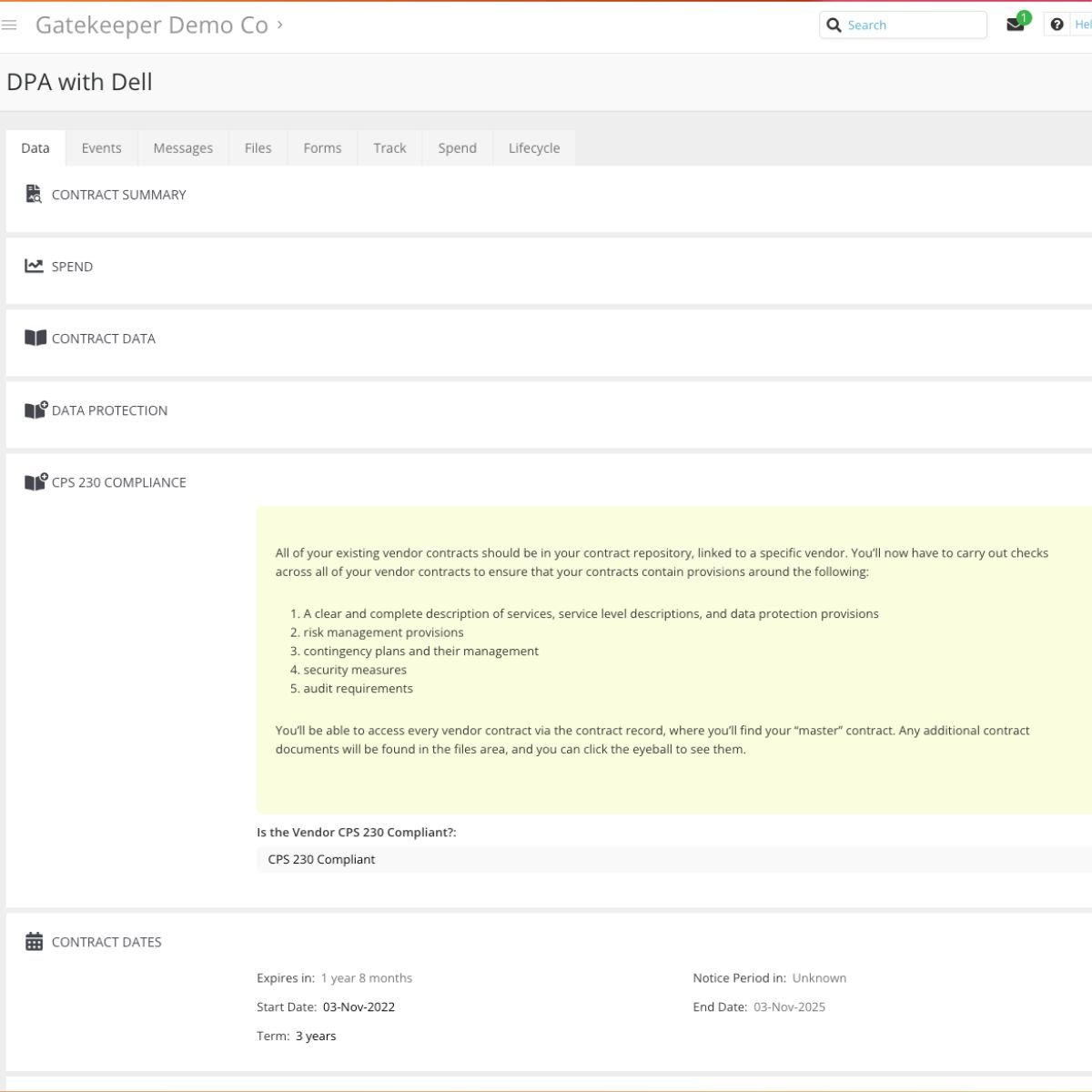 CPS 230 Compliance Status in the Vendor Record
CPS 230 Compliance Status in the Vendor Record
This is important because we can use this data point to report via “Saved Views” (one of my favourite Gatekeeper features) and pull partial and non-compliant contracts into a contract amendment workflow.
.png?width=1475&height=623&name=CPS%20Non-Compliance%20Saved%20Contract%20View%20(1).png) Contract amendment workflow
Contract amendment workflow
We can then create an APRA CPS 230-specific contract amendment workflow using our Best Practice Workflows and trigger the relevant contracts onto this card to begin the contract amendment process without vendors.
For new vendor contracts, it’s straightforward. You can make use of the contract review best practice workflow to carry out your:
As you review the contract, you can use the custom data point you’ve already created to signal the compliance level pre- and post-negotiation. This will force compliance; if any contract is anything less than compliant, you can prevent it from moving forward.
As part of your APRA compliance obligations, you’ll need to show that:
All of these can be impacted significantly by the vendors you choose. So the easiest way to gather this information is to carry out effective due diligence of every vendor. You can do this by using the vendor onboarding best practice workflow and creating a set of questions specific to CPS 230 to cover your compliance requirements.
If you want to report on this data, you’ll need to utilise custom data to create this (like we did with that contract compliance point).
You’ll now have to report on two key areas which are:
For Incident Management:
The Risk Module within Gatekeeper is the best place to track potential and current incidents. Ideally, you can preempt any potential incidents and build risk mitigations in collaboration with your vendors.
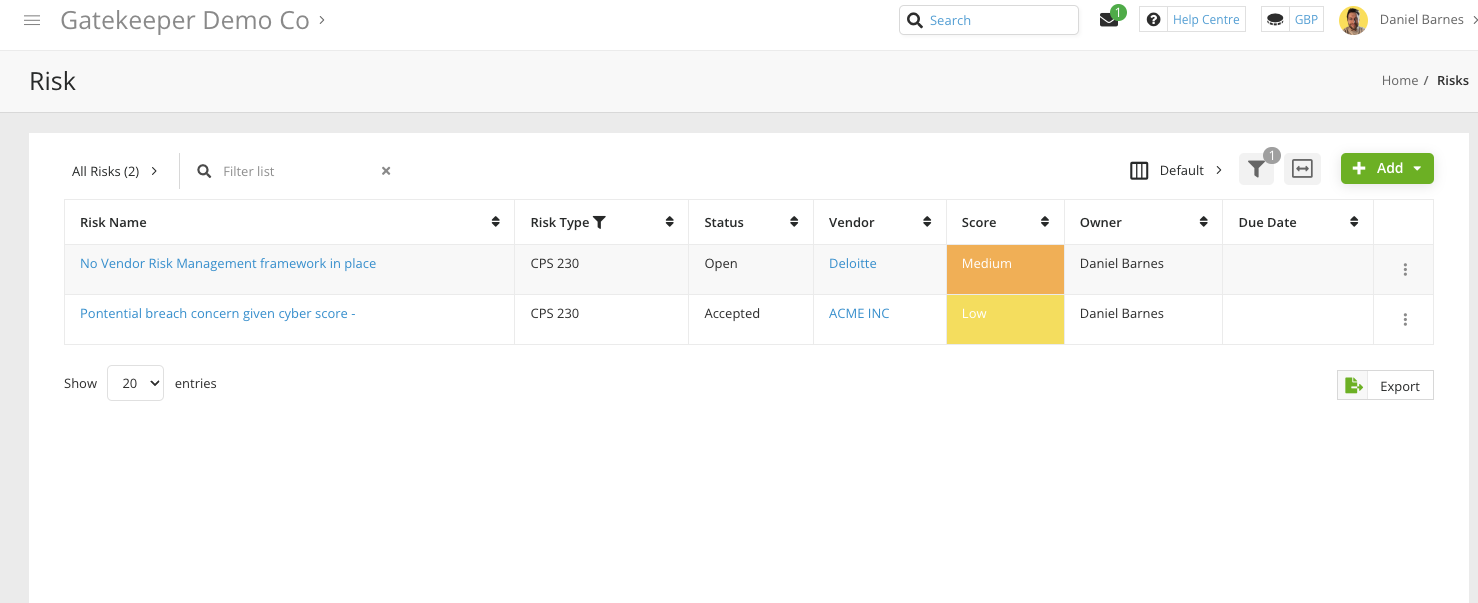 Gatekeeper's Risk Module
Gatekeeper's Risk Module
As part of your vendor onboarding process, you can ensure you get up-to-date copies of:
For each of these, we will use the File Expiration Best Practice Workflow to notify that the vendor needs to update their documentation and your team can review their updated positions, either rejecting them or approving them throughout the life of the vendor relationship.
For new vendors, you’ll need to ensure that your processes are capturing this information, and it would be beneficial to create a phase dedicated to risk capture and mitigation.
For existing vendors, you may need to get additional information from your vendors.
For Third-Party Risk Management:
We can use the Risk Register again, but I’ll take this further by utilising Gatekeeper’s Market IQ Suite.
With this, we can review and continuously monitor our vendors for credit, cyber, and OFAC risks 24/7/365. What’s great is that if we notice a downward trajectory in credit or cyber health, we can use automated workflows to kick-start a risk mitigation process.
From a reporting angle, all of this data is available in Saved Views, and a more detailed breakdown of risk history is available on each individual vendor record.
Every Vendor Management and Legal team understands the importance of oversight and effective processes to monitor risks and manage contracts.
If you haven’t already, ensure that you build out a clear vendor risk and contracting policy to satisfy this requirement. This might be a section within a wider piece that covers organisational risk (ideal), or your wider procurement process.
You can then ensure that the key requirements are built into your vendor and contract workflows to ensure you’ve covered everything.
Existing contracts with service providers must meet these requirements from the next renewal date or by 1st July 2026.
In short, all of your contracts from this date onwards need to be CPS 230 compliant. So you’ll need to build compliance checks into your contract renewal process. For any contract that is going to be renewed, you’ll need to make sure that everything else we’ve covered up to now is included.
We can do this by utilising our renewal process to review contracts and negotiate the required changes with the vendor to become compliant.For Existing Vendors
We’ll review every contract using LuminIQ to ensure that we’ve got a clear description in place. This will usually be found in the schedules, a Statement of Work, Data Processing Agreements, or a dedicated section of Service Level Agreements.
We can use the AI Summary in the Contract Record to get a sense of what each contract is about. If it isn’t pulling through, it’s likely the contract doesn’t have a clear description and needs work.
For any contract that isn’t compliant, much like we did with the earlier specific clauses, we will need to use the Contract Amendment Best Practice Workflow with our vendors to make these changes.
For New Vendors
This can be captured as part of your contract review phase. A useful tip would be to build this into your contract playbook and link to it within your guidance notes in your contract review phase. Additionally, you could create a checklist that is required to be completed before you can move the card onto a new phase.
APRA-regulated entities must also maintain a register of information on their ICT contracts and distinguish between those supporting critical functions and those that do not.
We can capture this information using that data point “Category” for our contracts.
We’ll create two categories here:
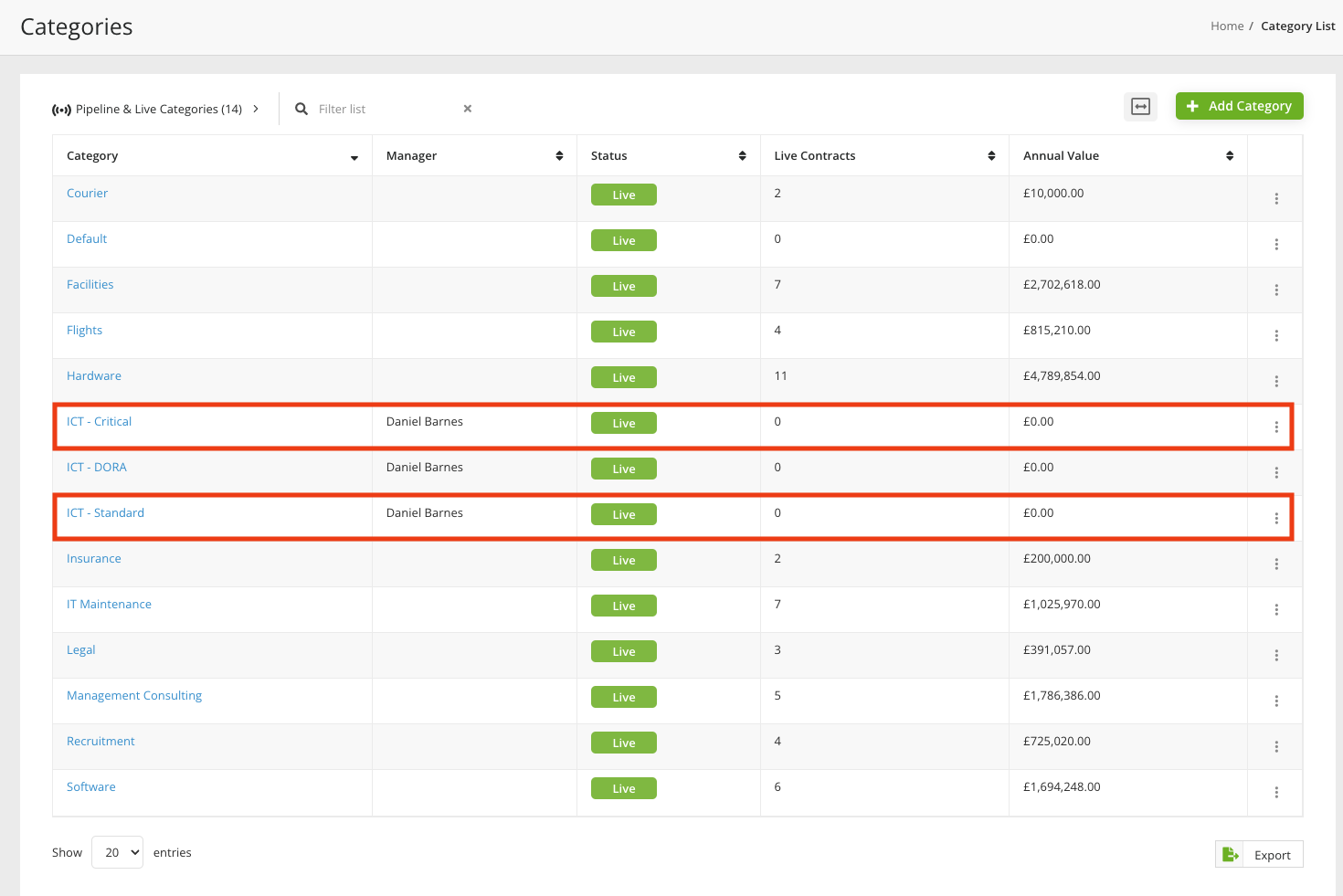 Create categories within Gatekeeper
Create categories within Gatekeeper
For new vendor contracts, you can capture this information during the contract review phase and include any guidance around categorising vendor contracts in the workflow.
You’ll need to:
Build a saved view within Gatekeeper
With CPS 230 now in force and existing agreements uplifted by 1 July 2026, the bar shifts from activity to assurance.
Boards expect a risk-first operating model, a single source of truth across third parties and agreements, and audit-ready evidence on demand.
Gatekeeper is the unified platform for contracting and third-party risk management: it screens providers before engagement, continuously monitors obligations and tolerances, and automates evidence capture via LuminIQ agents.
That way, you can control concentration risk, demonstrate resilience and satisfy APRA with confidence. If you’re ready to operationalise CPS 230 end-to-end, book a demo now and see how a unified approach turns compliance into control.
Ready to improve your contract & vendor management?
.png)
.png)
.png)
-4.png)
Before Gatekeeper, our contracts
Anastasiia Sergeeva, Legal Operations Manager, BlaBlaCar
were everywhere and nowhere.
Gatekeeper is that friendly tap on the shoulder,
Donna Roccoforte, Paralegal, Hakkasan Group
to remind me what needs our attention.
Great System. Vetted over 25 other systems
Randall S. Wood, Associate Corporate Counsel, Cricut
and Gatekeeper rose to the top.
Thank you for requesting your demo.
Next Step - Book a Call
Please book a convenient time for a quick call to discuss your requirements.