Achieving Modern Slavery Act Compliance with Vendor and Contract Automation
17:41
Regulation, Modern Slavery, Regulatory compliance
Shannon SmithFeb 11, 2025 9:43:55 AM
The Modern Slavery Act is legislation aimed at combating modern slavery, forced labour, and human trafficking within businesses and their supply chains.
This Act places a legal obligation on large companies operating in the UK to be transparent about their efforts to identify and address modern slavery risks. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties, including unlimited fines and reputational damage.
Ethical practices aren't just limited to the UK, though - especially when businesses have a globalised supply chain. This piece of legislation has recently been mirrored in Canada, where Bill S-211 (Fighting Against Forced Labour and Child Labour in Supply Chains Act), came into force on 1 January 2024.
By centralising vendor information, automating due diligence processes, and using powerful risk assessment tools, procurement teams can maintain transparency across their supply chains, demonstrate their commitment to ethical business practices and comply with the legislation.
In this article, we'll take a look at:
The Modern Slavery Act act aims to hold organisations accountable for identifying and preventing exploitative practices that deprive individuals of their freedom and dignity.
The Act defines modern slavery as encompassing various forms of exploitation, including slavery, servitude, forced or compulsory labour, and human trafficking.
It recognises that these practices can manifest in various sectors, from manufacturing and agriculture to hospitality and construction, and can occur both domestically and internationally.
The Modern Slavery Act applies to organisations operating in the UK with an annual turnover of £36 million or more. These organisations are required to publish an annual statement outlining the steps they have taken to ensure that their operations and supply chains are free from modern slavery practices.
However, the UK government has been actively reviewing the Modern Slavery Act, with particular focus on its applicability and enforcement. One of the key discussions revolves around expanding the due diligence requirements to cover all sectors and businesses, regardless of size.
By mandating detailed due diligence for all businesses, the government seeks to ensure that every organisation, regardless of scale, takes responsibility for identifying and mitigating risks of forced labour, human trafficking, and exploitative practices.
Such a change would mean that businesses across industries - large and small - would need to adopt comprehensive measures, including supply chain mapping, vendor risk assessments, and regular reporting.
To comply with the Modern Slavery Act, your organisation must fulfil several key requirements:
Failure to comply with the Modern Slavery Act can result in severe consequences for organisations:
By understanding the Modern Slavery Act, its applicability, key compliance requirements, and the consequences of non-compliance, your organisation can take proactive steps to address modern slavery risks and demonstrate its commitment to ethical business practices.
Achieving and maintaining compliance with the Modern Slavery Act can be a daunting task for businesses, particularly those with complex and extensive supply chains. Here are some of the key challenges they may face:
Many businesses today have intricate and global supply chains, with multiple tiers of vendors and suppliers spread across different countries and regions.
Gaining visibility into these extended supply chains and ensuring that every link adheres to ethical labour practices can be an arduous undertaking.
Mapping out the entire supply chain, identifying potential risks, and implementing effective due diligence measures can be resource-intensive and challenging.
Ensuring compliance with the Modern Slavery Act requires businesses to obtain and maintain up-to-date compliance documents from their vendors and suppliers.
As supply chains evolve, businesses must continually request and collect new or updated compliance documents from vendors.
This process can be time-consuming and prone to delays, as vendors may not prioritise providing these documents. They may also have their own internal processes that slow down the exchange of information.
Compliance with the Modern Slavery Act is not a one-time exercise; it requires ongoing vigilance and regular re-evaluation.
Businesses must continuously monitor their supply chains for any changes or potential risks that may arise, and they must reconfirm their vendors' compliance status at regular intervals.
This ongoing process can be resource-intensive and challenging to manage, especially for businesses with a large and dynamic supply chain.
Achieving compliance is a critical responsibility for your business, but relying on manual processes for vendor and contract management can significantly undermine these efforts.
Manual approaches are often slow, error-prone, and difficult to scale, leaving your organisation vulnerable to compliance risks.
It becomes challenging to consistently track vendor practices, verify supply chain transparency, or ensure all necessary checks are completed on time. Missing documentation, inconsistent record-keeping, and a lack of centralised oversight can lead to blind spots that expose your business to ethical and legal vulnerabilities. Automating those processes is essential for staying ahead of these challenges.
By implementing automation, your organisation can streamline due diligence workflows, maintain real-time visibility over its supply chains, and create reliable audit trails. Automated systems also enable proactive compliance by setting alerts for missing certifications, contract renewals, and key regulatory milestones - ensuring your team can focus on mitigating risks rather than managing paperwork.
Procurement professionals in regulated, scaling businesses often face significant challenges when it comes to complying with the Modern Slavery Act. Limited resources, manual processes, and expanding vendor networks can make it difficult to ensure supply chain transparency and uphold ethical standards.
Tracking compliance documentation, maintaining audit trails, and identifying potential risks can quickly overwhelm teams, leaving organisations vulnerable to compliance gaps.
Automation offers a powerful solution to these challenges, enabling procurement teams to simplify and streamline their compliance efforts. By reducing reliance on manual methods, automation helps eliminate inefficiencies, minimise human error, and ensure that critical compliance tasks are completed consistently and on time and that adherence to the Modern Slavery Act is achieved.
.png?width=720&height=496&name=How%20to%20automate%20Modern%20Slavery%20Act%20compliance%20-%20visual%20selection%20(1).png)
A common challenge for growing procurement teams is managing vast amounts of vendor information spread across spreadsheets, emails, and disconnected systems. This lack of organisation can lead to missed compliance deadlines, difficulty tracking vendor obligations, and inefficiencies when preparing for audits.
A centralised vendor and contract lifecycle management (VCLM) platform consolidates all vendor information in one secure and organised repository. This includes compliance documents, such as Modern Slavery Act statements, anti-slavery policies, and due diligence records. By centralising data, procurement professionals gain real-time visibility into their vendors' compliance statuses, making it easier to identify and address gaps.
Regulated organisations must demonstrate compliance through detailed audit trails and thorough documentation. However, using manual data capture can make it a struggle to maintain accurate records across a growing vendor base. Version control issues, missing documentation, and limited visibility into past actions can create significant challenges during audits or legal reviews.
Automating document management ensures that all compliance-related materials are accurately stored and easily accessible. Version control capabilities track updates over time, creating a clear audit trail of actions taken. This supports compliance and demonstrates your organisation's proactive approach to ethical supply chain management.
Managing vendor compliance can be a logistical challenge, particularly for procurement teams juggling large vendor networks. Chasing documents, clarifying requirements, and ensuring timely responses often lead to delays and frustration for both teams and vendors.
A dedicated vendor portal can help address these pain points by creating a centralised, self-service hub for vendors to manage their compliance obligations.
Through the portal, vendors can securely upload compliance documents and easily view their compliance status. It allows them to see which documents are pending, expired, or require updates, while automated notifications ensure that they are reminded of upcoming deadlines or missing information.
Create transparency, foster accountability, and ensure that all stakeholders are aligned in meeting ethical and regulatory requirements. By empowering vendors to take ownership of their compliance with the Modern Slavery Act, your team can focus on higher-level strategy while maintaining control over key processes.
Compliance with the Modern Slavery Act often involves multiple steps, from initial vendor onboarding to final approvals for documentation or risk assessments. Managing these workflows manually can lead to delays, miscommunication, and the risk of critical tasks being overlooked.
Automated approval workflows help simplify and standardise the process. Each step in the workflow can be configured to match your organisation's specific requirements, ensuring tasks are automatically assigned to the right stakeholders at the right time. For example, a due diligence review might be routed to legal, while vendor approval could require sign-off from procurement or compliance teams.
These workflows maintain accountability by tracking each stage of the process, highlighting pending actions, and ensuring that nothing slips through the cracks.
Automated notifications keep everyone informed about their responsibilities and deadlines, allowing teams to manage complex compliance requirements with ease. By reducing reliance on manual coordination, automated workflows help reinforce transparent, auditable processes that show your organisation's commitment to ethical practices.
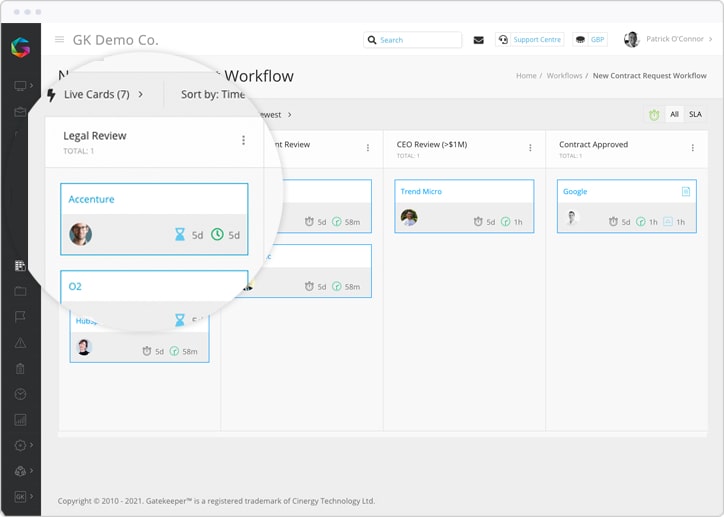
Busy procurement teams cannot often continuously monitor and assess risks across their entire supply chain. This creates vulnerabilities, especially when working with vendors in high-risk regions or industries. Without the right tools, potential red flags can go unnoticed until they escalate into compliance breaches.
Automated risk assessment tools can help overcome this challenge by enabling teams to define custom risk criteria that reflect their organisation's unique priorities. Factors like geographic location, industry sector, or past compliance issues can be automatically scored and flagged. Alerts for changes in vendor status or emerging risks empower procurement teams to take swift, informed action before issues escalate.
Visual dashboards also make it easier to monitor risks across the supply chain, presenting data in an accessible way. This offers a clear picture of risk without requiring extensive manual analysis.
By automating key aspects of Modern Slavery Act compliance, procurement teams can overcome resource constraints, maintain supply chain transparency, and confidently meet regulatory obligations. Automation empowers teams to focus on strategic initiatives while ensuring that ethical practices remain at the heart of their operations.
Key benefits of automating Modern Slavery Act compliance include:
Take the first step towards ensuring ethical and responsible business practices by requesting a demo of Gatekeeper today. Discover how our platform can simplify the process of achieving compliance with the Modern Slavery Act, mitigate risks, and foster a culture of transparency and accountability within your organisation.

Shannon Smith bridges the gap between expert knowledge and practical VCLM application. Through her extensive writing, and years within the industry, she has become a trusted resource for Procurement and Legal professionals seeking to navigate the ever-changing landscape of vendor management, contract management and third-party risk management.
Sign up today to receive the latest GateKeeper content in your inbox.
.png)
.png)
.png)
-4.png)
Before Gatekeeper, our contracts
Anastasiia Sergeeva, Legal Operations Manager, BlaBlaCar
were everywhere and nowhere.
Gatekeeper is that friendly tap on the shoulder,
Donna Roccoforte, Paralegal, Hakkasan Group
to remind me what needs our attention.
Great System. Vetted over 25 other systems
Randall S. Wood, Associate Corporate Counsel, Cricut
and Gatekeeper rose to the top.
Thank you for requesting your demo.
Next Step - Book a Call
Please book a convenient time for a quick call to discuss your requirements.